Companies are moving most of their services towards cloud platforms. This trend has taken a positive turn with the global COVID pandemic. As most of the companies (and their employees) are working remotely, they are going for cloud deployment solutions. There are different cloud computing models available in the market. The choice of an ideal cloud model will differ with your needs. We will be discussing two such models Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS) through this blog.
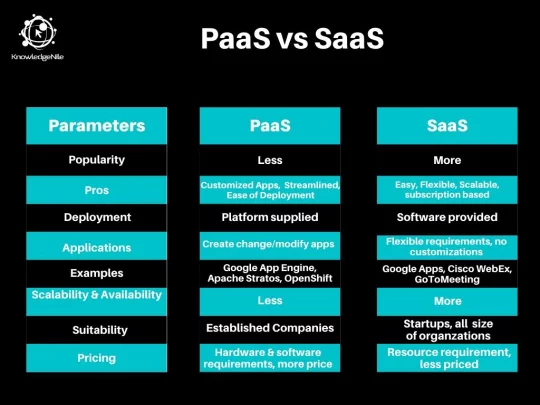
PaaS vs. SaaS: Key Differentiating Points
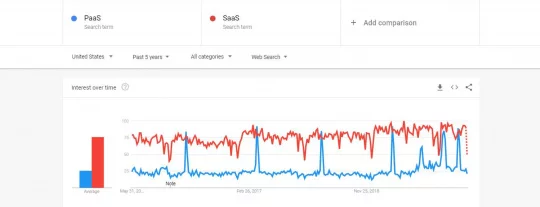
From the above-mentioned graph, we can see that SaaS is a more popular tool among the two as per the Google search trends.
But, we can also see that there are certain periods when PaaS has a spiked interest, and it has crossed SaaS in terms of search queries. Overall, over the five year period, SaaS has turned out to be more popular.
Platform-as-a-service, commonly known as PaaS, is a cloud computing platform that provides companies with the frameworks required for application development.
Essentially, in simpler words, it provides a platform for a developer to work on his/her skills without having to worry about the tools.
On the other hand, software-as-a-service, commonly known as SaaS, is a cloud computing platform that provides users with the software for the team. Typically, it is a subscription model hosted on the cloud platform that you can rent for a certain period of time.
PaaS is more useful when you have many people working on the same project. It is most useful when you need to create custom applications for your own use or for a client.
You have the flexibility to create change/modify or create your own applications on PaaS.
With SaaS, it is not possible to create your own custom applications as you are using third-party software. SaaS is primarily an OPEX (Operation Expenditure) category platform.
Hence, if you don’t have enough resources to create your own applications, SaaS is an ideal fit for you. Also, if you are a startup and don’t want to invest in capital extensive resources, SaaS can be an answer to your queries.
Key examples of PaaS include Google App Engine, Apache Stratos, OpenShift, Windows Azure, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, etc.
The key examples of SaaS include Google Apps, CAD software, Cisco WebEx, GoToMeeting, Hubspot, Zendesk, Office 365, Adobe Creative Cloud, etc.
PaaS is scalable, but it has limitations on the scaling. PaaS is also highly available most of the time. Its availability is hampered only with the data outages or issues at the provider’s end.
SaaS is much easier to scale up and scale down as per the requirements as the service provider provides you the complete software. SaaS is highly available, and it can be unavailable only when the service provider doesn't have multiple data center backups.
PaaS is more suitable to the established organizations that have their entire infrastructure ready. Also, it is more suitable for the organizations that typically have custom needs and rely on their IT team to provide it.
On the other hand, SaaS is suitable for all sizes of organizations as it is highly scalable and available.
Also, as the costs involved with SaaS are much less, companies tend to go for a SaaS solution wherever they don’t need customizations.
You may also like: CaaS vs. PaaS: Understand the Difference Between two
Pros of PaaS:
- Ability to create customized applications.
- Streamlines the processes easily.
- Easily speed up the development and deployment of applications.
Cons of PaaS:
- Lock-in period.
- Less flexibility.
- More skills required.
Pros of SaaS:
- Ease of Use.
- Flexibility
- Scalability
- Lesser lock-in period.
- Minimal skillset is required.
- Cost-friendly
Cons of SaaS:
- No control over applications.
- Data security issues may occur.
- Compatibility with other tools.
- No or minimum customization options.
Most of the PaaS platforms offer a free tier to the new users. After the free trial is over, the users are charged on the basis of the plan they have chosen.
These plans vary from one provider to another, but basically, they are dependent upon the hardware and the software requirements. The typical lock-in periods are on the higher side.
While on the other hand, many of the SaaS tools also offer free trials for a said period of time. Most of the SaaS tools are available on monthly subscription plans. The pricing differs upon the usage, utility and applications as well. But, overall, you have to pay less amount with SaaS.
Key Takeaways
We hope this comparison between PaaS & SaaS will help you understand the basic difference, applications, deployment methods, and utility.
These platforms can co-exist with one another, and you may end up choosing both the solutions for different requirements as many of us have.
Also Read: Top Five Difference between Iaas & PaaS 2018